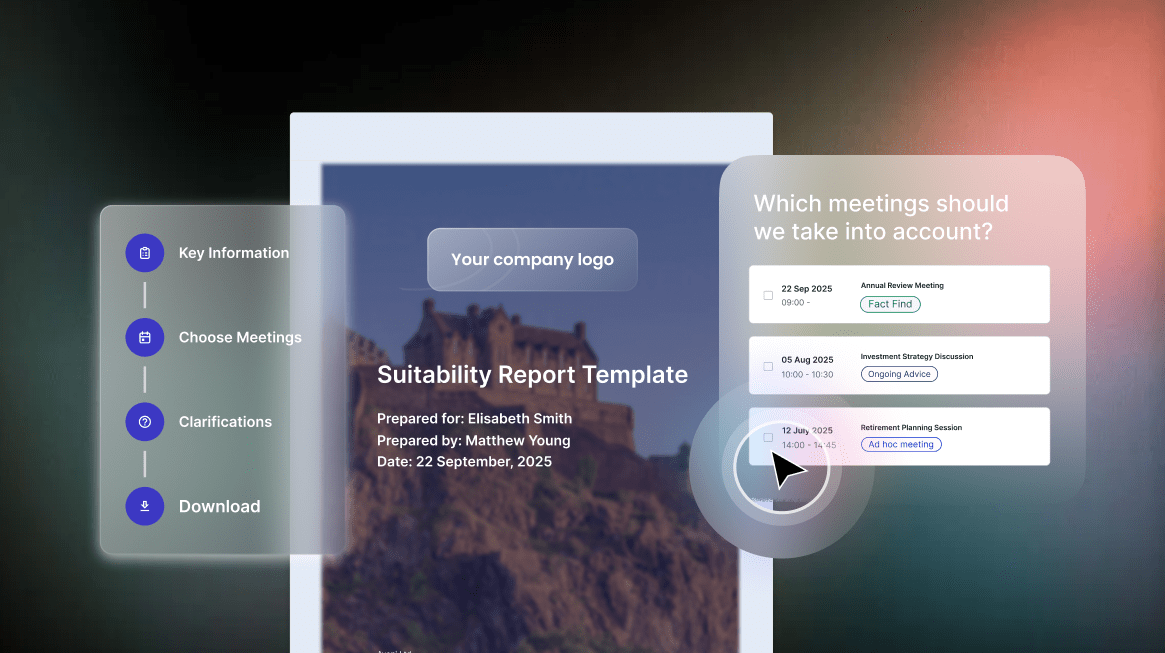
Automated suitability report writing requires seamless CRM integration to access client data, pull fact-find information and update records automatically. UK financial advisers typically need integration with intelliflo office, Xplan, Salesforce Financial Services Cloud or other platforms.
Why CRM Integration Matters
AI-powered suitability report writing depends on comprehensive client information to generate accurate, complete documentation.
Client data access allows the system to retrieve current circumstances, financial position, goals, risk profile and previous advice. This context enriches reports beyond information captured in individual meetings.
Fact-find integration pulls detailed client information including income, expenditure, assets, liabilities, protection needs and objectives. The AI combines fact-find data with meeting discussion to create comprehensive suitability documentation.
Previous interaction history provides context about ongoing relationships, past recommendations and client communication preferences. The system understands how current advice fits within the broader advisory relationship.
Automatic updates ensure CRM records reflect meeting outcomes without manual data entry. The system records new information, updates changed circumstances and maintains current client profiles.
One advice network calculated that CRM integration eliminated 15 to 20 minutes of manual data entry per client meeting across their 200-adviser population, saving 6,000 to 8,000 hours annually.
Core Integration Capabilities
Effective CRM integration requires specific technical and functional capabilities.
API connectivity enables automated data exchange between the suitability report system and CRM platform. Modern APIs support real-time synchronisation, secure data transfer and reliable performance.
Bi-directional sync ensures information flows both ways. The suitability report system reads client data from the CRM and writes meeting outcomes, report summaries and updated information back to client records.
Field mapping matches CRM data fields to report requirements. The integration must know where to find client age, risk profile, investment objectives and other information within the CRM structure.
Data transformation handles differences in format, terminology and structure between systems. The integration converts CRM data into formats the suitability report system requires and vice versa.
UK Platform-Specific Requirements
Different UK CRM platforms require specific integration approaches.
Intelliflo office integration typically uses API connections accessing client records, fact-finds, contact notes and document storage. The system must handle intelliflo’s specific data structures and terminology.
Xplan integration connects through APIs or XML data exchange depending on implementation. The integration pulls plan data, fact-find information and client relationship details.
Salesforce Financial Services Cloud integration leverages standard Salesforce APIs with financial services-specific objects and fields. The system must understand Salesforce’s relationship model and data architecture.
FNZ integration for wealth platforms requires connections to underlying CRM systems and potentially direct platform integration for account information.
Data Access Patterns
CRM integration supports different data access patterns throughout the advice process.
Pre-meeting data pull retrieves client information before meetings begin. Advisers and AI systems review current circumstances, previous advice and outstanding actions to prepare for discussions.
Real-time access during meetings allows the system to reference client data, verify information and identify changes in circumstances whilst conversations occur.
Post-meeting updates write new information gathered during meetings back to CRM records. This maintains current client profiles without manual data entry.
Ongoing synchronisation ensures CRM data and suitability report system information remain aligned. Changes in either system propagate to maintain consistency.
Information Categories Requiring Integration
Specific client information categories must be accessible through CRM integration.
Personal details including name, date of birth, contact information, marital status, dependants and employment status provide basic client context.
Financial information covers income, expenditure, assets, liabilities, existing provisions, pensions and protection policies. This data informs suitability assessments.
Goals and objectives including retirement plans, education funding, inheritance intentions and short-term needs guide recommendation development.
Risk profile comprising attitude to risk, capacity for loss, investment experience and time horizon determines suitable product selection.
Previous advice history including past recommendations, implemented solutions and ongoing reviews provides continuity context.
Security and Compliance Considerations
CRM integration must meet strict data protection and regulatory requirements.
UK GDPR compliance ensures client data transfers between systems occur securely, consent is obtained appropriately and data processing meets regulatory standards.
Encryption protects data during transmission between CRM and suitability report systems. Industry-standard protocols prevent unauthorised access.
Access controls limit which users can read or modify client information. Role-based permissions ensure advisers access only appropriate client records.
Audit trails log all data access and modifications. These records support regulatory reviews and internal monitoring.
One firm’s compliance team required detailed audit specifications before approving CRM integration. The implementation included comprehensive logging of all data exchanges between systems.
Integration Architecture Options
Firms can implement CRM integration through different technical approaches.
Direct API integration connects suitability report systems to CRM platforms through vendor-provided APIs. This approach offers real-time data access and automated synchronisation.
Middleware solutions provide intermediary platforms managing data exchange between systems. Middleware handles transformation, error management and integration monitoring.
File-based integration uses scheduled data exports and imports when real-time connection is not possible. This approach suits legacy CRM systems lacking modern APIs.
Hybrid architectures combine multiple integration methods for different data types or use cases. Critical data syncs in real time whilst historical information transfers through batch processes.
Implementation Complexity Factors
Several factors affect CRM integration implementation difficulty and timeline.
CRM platform age influences integration options. Modern cloud-based platforms offer robust APIs. Legacy on-premise systems may require custom development.
Data quality in existing CRM affects integration success. Clean, structured data integrates smoothly. Inconsistent or incomplete records require remediation before or during implementation.
Customisation level impacts integration complexity. Heavily customised CRM deployments need bespoke integration work. Standard configurations integrate more quickly.
Network structure matters for multi-site advice firms. Centralised CRM deployments simplify integration. Federated systems with multiple CRM instances increase complexity.
One advice network with three separate CRM systems from acquisitions required parallel integration projects. A unified CRM would have simplified deployment substantially.
Testing and Validation
Comprehensive testing ensures CRM integration performs reliably before production deployment.
Data accuracy testing verifies that information transfers correctly between systems. Sample client records are processed and results validated against source data.
Field mapping validation confirms all required information flows to appropriate locations. Missing mappings or incorrect assignments are identified and corrected.
Update testing ensures changes in one system propagate correctly to the other. Test scenarios cover various update types and edge cases.
Performance testing validates that integration handles expected data volumes without delays. Response times and system load are measured under realistic conditions.
Error handling verification confirms that integration failures are detected, logged and managed gracefully without data corruption.
Ongoing Maintenance Requirements
CRM integration requires continuous maintenance to ensure reliable operation.
Platform updates from CRM or suitability report vendors may affect integration. Monitoring release notes and testing upgrades prevents disruption.
Data quality monitoring identifies issues affecting integration performance. Regular audits catch problems before they impact adviser productivity.
Error log review detects integration failures requiring investigation. Proactive monitoring prevents small issues from becoming major problems.
Performance optimisation adjusts integration configuration as data volumes and usage patterns evolve. Periodic tuning maintains responsive operation.
Benefits of Effective Integration
Well-implemented CRM integration delivers substantial advantages beyond automated report writing.
Eliminated double data entry saves 15 to 20 minutes per meeting across adviser populations. Time freed from administrative work redirects to client-facing activities.
Improved data accuracy reduces errors from manual transcription. Automated data flow ensures consistency between systems.
Enhanced compliance provides complete audit trails showing how client information informed advice. Regulatory reviews proceed smoothly when data lineage is clear.
Better adviser experience results from seamless workflows without system switching. Advisers work more efficiently when information flows automatically.
Common Integration Challenges
Firms implementing CRM integration face predictable obstacles with established solutions.
Legacy CRM limitations may restrict integration options. Upgrading platforms or implementing middleware overcomes these constraints.
Data inconsistencies between systems require resolution. Standardising terminology, formats and structures before integration improves results.
Vendor cooperation varies in providing integration support and documentation. Working with vendors experienced in UK financial advice ensures smoother implementation.
Change management helps advisers adapt to integrated workflows. Training on how systems work together accelerates adoption.
Vendor Selection Criteria
Firms should evaluate CRM integration capabilities when selecting suitability report automation vendors.
Pre-built integrations with your specific CRM platform reduce implementation time and cost. Vendors with existing connectors to intelliflo, Xplan or Salesforce deploy faster.
Integration track record in UK financial advice indicates whether the vendor understands local requirements. Ask for client references using similar CRM platforms.
Technical capabilities including API quality, data transformation flexibility and error handling determine integration robustness.
Support quality for integration issues affects ongoing success. UK-based technical support familiar with UK CRM platforms responds more effectively.
Future Integration Capabilities
CRM integration continues evolving with new capabilities emerging.
Predictive data population may suggest information advisers should update in CRM based on meeting discussions. The system recommends changes rather than only automating known transfers.
Intelligent conflict resolution could handle situations where CRM data contradicts meeting information. The system might flag discrepancies for adviser resolution rather than overwriting automatically.
Extended ecosystem integration beyond CRM to back-office platforms, document management and other adviser systems creates comprehensive workflow automation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can automated suitability report writing work without CRM integration? Yes, but with reduced efficiency. The system can generate reports from meeting transcripts alone but advisers must manually add client context. Integration delivers substantially better results.
What if our CRM is heavily customised? Custom CRM configurations require tailored integration work. Implementation takes longer and costs more but remains achievable with experienced vendors.
How long does CRM integration implementation take? Standard integrations with common UK platforms typically complete within 4 to 6 weeks. Customised or legacy CRM systems may require 8 to 12 weeks.
What happens if CRM integration fails during normal operation? Well-designed integrations include error handling and fallback processes. Advisers receive alerts about failures and can proceed manually whilst technical teams resolve issues.
Learn how Aveni Assist integrates with UK CRM platforms for seamless suitability report automation →