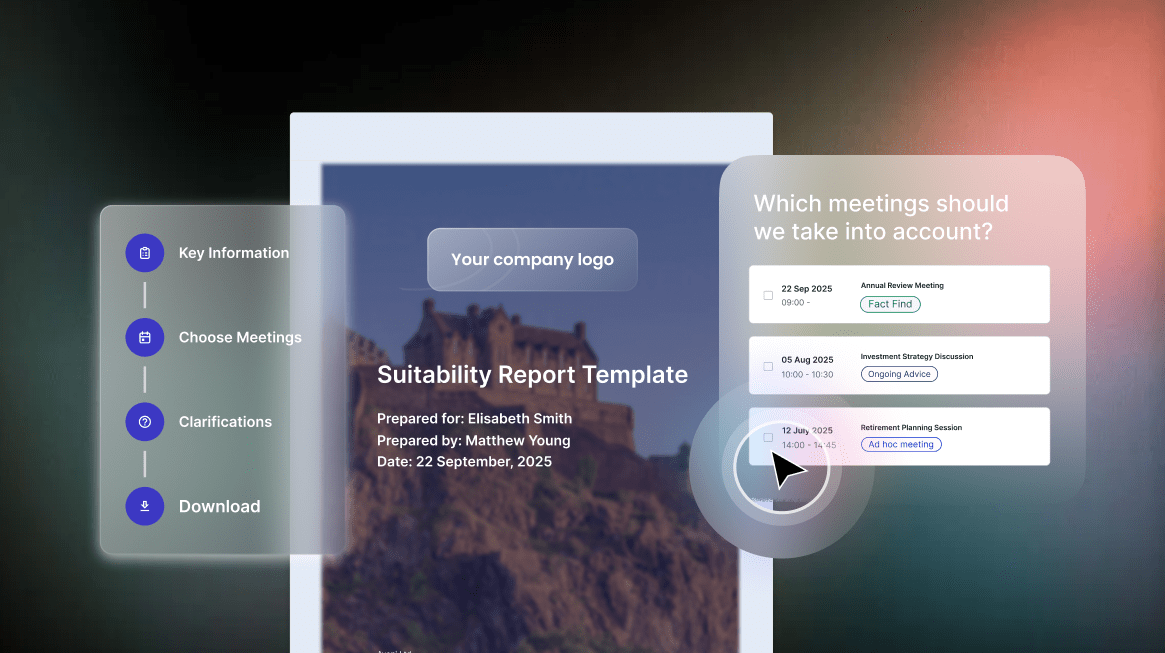
The UK financial services landscape is undergoing one of the most significant shifts in decades. Regulators are introducing a new category of service called targeted support, designed to sit between generic guidance and full regulated financial advice. This evolution reflects widespread concern that too few consumers currently receive formal financial advice with only a small minority engaging advisers each year.
Understanding the differences between targeted support and regulated advice is critical for firms planning services, hiring, compliance, and technology strategies. Below, we explain the core distinctions, why they matter, and how firms can adapt.
The Advice Gap: Why Something New Is Needed
The UK has a persistent “advice gap” — a term used to describe the large number of consumers who need help with financial decisions but do not receive regulated financial advice.
According to the Financial Conduct Authority’s Financial Lives 2024 survey, fewer than 9% of adults accessed regulated financial advice about pensions, investments or retirement planning in the past year.
This low take-up persists despite many consumers having assets to manage and long-term financial decisions to make. Targeted support is intended to help close that gap by offering an accessible, affordable alternative for consumers who do not require full personalised advice.
What Is Targeted Support?
Targeted support is a new form of regulated support being introduced by the UK Government and the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) as part of the Advice Guidance Boundary Review.
Under this regime, FCA-authorised firms will be able to:
-
Define consumer segments based on shared characteristics
-
Develop ready-made suggestions aimed at those segments
-
Deliver those suggestions to individual consumers without conducting full individual suitability assessments
Targeted support is not a replacement for regulated advice; instead, it fills the space between generic guidance (such as Pension Wise or general online content) and personalised financial advice.
Key Differences: Targeted Support vs Regulated Advice
Though both services fall under the FCA’s regulatory umbrella, they differ significantly in terms of scope, assessment, regulatory obligations, delivery model, and cost.
1. Assessment Requirements
Regulated Advice
-
Requires a comprehensive assessment of an individual’s full financial circumstances: income, expenditure, assets, liabilities, risk profile, goals, and personal factors.
-
Advisers must gather detailed information to ensure suitability of recommendations.
Targeted Support
-
Involves enough information to place a consumer into a predefined segment.
-
Does not require deep individual fact-finding or a complete suitability assessment.
-
Focuses on group-based appropriateness rather than personal tailoring.
2. Type of Recommendations
Regulated Advice
-
Personal recommendations tailored to a specific individual’s financial situation.
-
Advisers usually provide a full suitability report and are responsible for demonstrating why a recommendation is right for that client.
Targeted Support
-
Suggestions are designed for groups sharing similar circumstances.
-
The recommendation is framed around what’s suitable for people like you, not what’s uniquely right for you as an individual.
-
There are limits on complexity; ready-made suggestions are typically for straightforward decisions.
3. Regulatory Obligations and Compliance
Regulated Advice
-
Governed by established FCA rules, including COBS (Conduct of Business Sourcebook) suitability requirements.
-
Requires detailed documentation, ongoing reviews, and suitability reports.
-
Advisers bear responsibility for ensuring recommendations fit individual needs.
Targeted Support
-
Regulated under a separate framework with conduct standards emphasising group outcomes.
-
Documentation focuses on how customers are assigned to segments and which suggestions were provided.
-
Firms must demonstrate that the suggestions are appropriate for the defined segments and deliver good outcomes.
4. Delivery Model and Scalability
Regulated Advice
-
One-to-one, personalised adviser interactions.
-
Time and cost intensive, typically reserved for clients with higher investable assets.
Targeted Support
-
Designed for one-to-many delivery.
-
Scales more efficiently, with digital platforms and automation playing a central role.
-
Enables firms to reach consumers who would otherwise not access advice due to cost or complexity.
5. Cost and Consumer Access
Regulated Advice
-
Typically commands higher fees reflecting advisor expertise and depth of analysis.
-
Asset thresholds and cost considerations make it inaccessible for many consumers.
Targeted Support
-
Lower cost or even free at the point of use in some models.
-
Designed to be affordable for consumers with modest assets or straightforward needs.
-
Part of a broader strategy to make support accessible to more people.
Why Targeted Support Matters
Targeted support is not intended to make individual financial advice obsolete. Instead, it creates a continuum of support options, from general guidance through targeted, simplified, and full regulated advice, helping consumers access the level of help appropriate to their needs and circumstances.
It acknowledges that:
-
Many consumers will never seek or afford full personalised advice.
-
Group-based suggestions can still improve decision-making.
-
Technology and structured approaches can deliver compliant outcomes at lower cost.
Implementation Timeline and Regulatory Context
The FCA’s Advice Guidance Boundary Review has been underway since 2023, with consultations and draft proposals shaping the emerging targeted support regime. Final rules are expected to take effect in early April 2026, with firms able to apply for permission from March 2026.
This has been described as one of the most significant reforms to the financial advice and support framework in over a decade.
What This Means for Advice Firms
Firms need to consider:
-
Whether targeted support fits their business model
-
How to design customer segments and suggestion frameworks that meet regulatory conduct standards
-
What qualifications and training staff will need
-
How to integrate technology to deliver efficient and compliant services
Firms may choose to offer targeted support as a stand-alone service, alongside regulated advice, or as a stepping stone toward full advice when individual client needs become more complex.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can targeted support replace regulated financial advice?
No. Targeted support does not provide personalised recommendations; it complements regulated advice by offering accessible, affordable help for common financial situations.
Will firms need FCA permission to offer targeted support?
Yes. Firms must obtain the relevant regulatory permissions and meet bespoke conduct standards before offering targeted support after the regime goes live in 2026.
Does targeted support require technology?
While not mandatory, technology and automation are central to delivering targeted support at scale and ensuring consistent compliance and documentation.
Learn how Aveni enables efficient delivery of both targeted support and regulated advice →